Hyundai Genesis (DH): Engine Control System / Description and Operation
Hyundai Genesis (DH) 2013-2016 Service Manual / Engine Control / Fuel System / Engine Control System / Description and Operation
| OBD-II review |
1. Overview
The California Air Resources Board (CARB)launched the
regulation of OBD (On Board Diagnostics) for vehicles sold in California
starting with the 1988 model year.
The first phase, OBD-I, required monitoring of the fuel
metering system, Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system and additional
emission related components. The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) was
required to light and alert the driver of the fault and the need for
repair of the emission control system. Associated with the MIL was a
fault code or Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) identifying the specific
area of the fault.
The OBD system, identifying vehicles exceeding emission
standards, was proposed by CARB to improve air quality. Passage of the
Federal Clean Air Act Amendments in 1990 has also prompted the
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to develop On Board Diagnostic
requirements. CARB OBD-II regulations were not introduced until 1999
when the federal regulations were in place.
The OBD-II system meets government regulations by monitoring
the emission control system. When a system or component exceeds emission
threshold or a component operates out of tolerance, a DTC will be
stored and the MIL illuminated.
The diagnostic executive is a computer program in the Engine
Control Module (ECM) or PowertrainControl Module (PCM) that coordinates
the OBD-II self-monitoring system. This program controls all the
monitors and interactions, DTC and MIL operation, freeze frame data and
scan tool interface.
Freeze frame data describes stored engine conditions, such as
state of the engine, state of fuel control, spark, RPM, load and warm
status at the point the first fault is detected. Previously stored
conditions will be replaced only if a fuel or misfire fault is detected.
This data is accessible with the scan tool to assist in repairing the
vehicle.
The center of the OBD-II system is a microprocessor called the Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module(PCM).
The ECM or PCM receives input from sensors and other
electronic components (switches, relays, and others) based on
information received and programmed into its memory (keep alive random
access memory, and others), the ECM or PCM generates output signals to
control various relays, solenoids and actuators.
2. Configuration of hardware and related terms
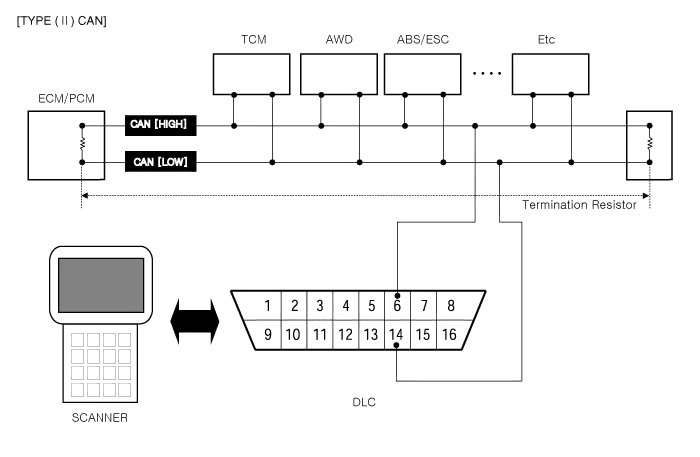
1) GST (Generic scan tool)
2) MIL (Malfunction indication lamp) - MIL activity by transistor
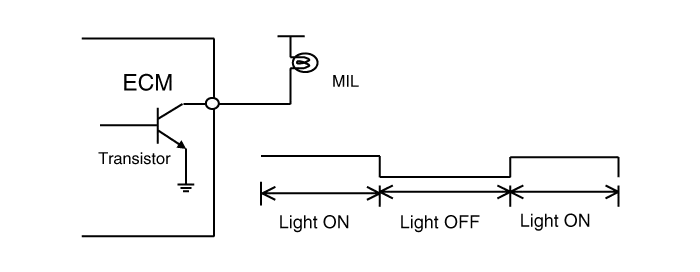
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) is connected between ECM
or PCM-terminal Malfunction Indicator Lamp and battery supply (open
collector amplifier).
In most cars, the MIL will be installed in the instrument panel. The lamp amplifier can not be damaged by a short circuit.
Lamps with a power dissipation much greater than total
dissipation of the MIL and lamp in the tester may cause a faulty
indication.
? At ignition ON and engine revolution (RPM)< MIN. RPM, the MIL is switched ON for a visual check by the driver.
3) MIL illumination
When the ECM or PCM detects a malfunction related emission
during the first driving cycle, the DTC and engine data are stored in
the freeze frame memory. The MIL is illuminated only when the ECM or PCM
detects the same malfunction related to the DTC in two consecutive
driving cycles.
4) MIL elimination
| |
Components Location 1. ECM (Engine Control Module)2. Barometric Pressure Sensor (BPS)3. Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS)4. Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS)5.
Other information:
Hyundai Genesis (DH) 2013-2016 Service Manual: Components and Components Location
C
Hyundai Genesis (DH) 2013-2016 Service Manual: Blind Spot Detection Switch Repair procedures
Removal 1. Disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal. 2. Remove the crash pad lower panel. (Refer to Body - "Crash Pad") 3. Remove the blind spot detection (BSD) switch (A) after disengaging the mounting clip. Installation 1. Install the crash pad side switch assembly after connecting the connector.
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Hyundai Genesis Owners Manual
- Hyundai Genesis Service Manual
- Smart Cruise Control Unit Repair procedures
- Brake System
- Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS) Repair procedures
- New on site
- Most important about car
Copyright В© 2026 www.hgenesisdh.com - 0.0244
